Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of data science, a transformative shift is occurring with the advent of Edge AI. This technology brings the power of artificial intelligence (AI) closer to where data is generated – at the edge of the network. By processing data locally on devices rather than relying on centralised cloud servers, Edge AI offers numerous benefits, including reduced latency, improved privacy, and increased efficiency. This article explores the fundamentals of Edge AI, its applications, and its impact on various industries.
Understanding Edge AI
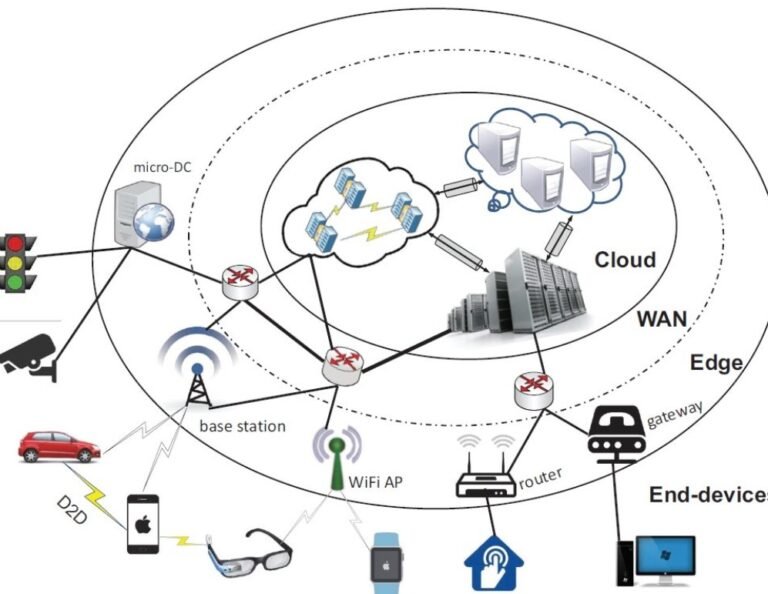
Edge AI refers to the deployment of AI algorithms on local devices or edge nodes, such as smartphones, IoT devices, and sensors, enabling them to process data in real-time. Unlike traditional AI models that rely on cloud computing, Edge AI leverages local computational resources to analyse and act on data at the source of its generation. This decentralised approach addresses several limitations associated with cloud-based AI, such as latency, bandwidth constraints, and data privacy concerns. Organisations often encourage their employees to learn Edge AI by sponsoring a Data Science Course that equips them with skills in this technology. This way, they ensure that they need not rely entirely on cloud computing that has some serious setbacks in spite of its advantages.
Key Components of Edge AI
Here are some key components of Edge AI.
Edge Devices: These are the hardware components located at the edge of the network, including sensors, cameras, smartphones, and industrial machines. They generate and collect data, which is then processed locally.
Edge Computing: This involves the use of local computational resources to process and analyse data on edge devices. Edge computing frameworks and platforms enable efficient execution of AI algorithms on these devices.
AI Models: Lightweight and optimised AI models are designed to run on edge devices with limited computational power. Techniques such as model compression, quantisation, and pruning are used to reduce the size and complexity of these models without compromising performance.
Connectivity: While edge devices process data locally, they often communicate with centralised cloud servers for further analysis, model updates, and storage. Hybrid architectures combine the benefits of edge and cloud computing.
Applications of Edge AI
Edge AI has a wide range of applicability which is why it is a much sought-after learning that is covered in an advanced Data Science Course in Chennai, Hyderabad, Bangalore and such cities where learning centres cater to the demand among professionals for the latest technologies.
Smart Cities: Edge AI is revolutionising urban infrastructure by enabling real-time data processing for applications like traffic management, surveillance, and waste management. For example, smart traffic lights equipped with AI can analyse traffic patterns and adjust signals in real-time to reduce congestion.
Healthcare: In healthcare, Edge AI enhances patient care through remote monitoring and diagnostics. Wearable devices and smart medical equipment can analyse vital signs and detect anomalies in real-time, alerting healthcare providers to potential issues immediately. This is particularly useful in managing chronic conditions and supporting elderly care.
Manufacturing: Edge AI is driving the transformation of the manufacturing sector by enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and automation. Industrial machines equipped with AI sensors can monitor their own performance, predict failures, and optimise production processes, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
Retail: Retailers are leveraging Edge AI to enhance customer experiences and optimise operations. Smart shelves and cameras equipped with AI can track inventory levels, analyse shopper behaviour, and provide personalised recommendations. This real-time data processing helps retailers manage stock more effectively and improve customer satisfaction.
Autonomous Vehicles: Edge AI is critical for the operation of autonomous vehicles, which require real-time processing of vast amounts of data from sensors and cameras. By processing data locally, these vehicles can make instantaneous decisions, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Agriculture: In agriculture, Edge AI is being used to optimise crop management, monitor soil conditions, and automate irrigation systems. Drones and sensors equipped with AI can analyse environmental data and provide farmers with actionable insights to improve yield and resource management.
Benefits of Edge AI
Edge AI has several benefits over traditional computing models making it a preferred upskilling option across business domains as evident from the large-scale enrolment a Data Science Course that includes Edge AI attracts. Here are some key benefits briefly described.
Reduced Latency: By processing data locally, Edge AI minimises the delay between data generation and analysis, enabling real-time decision-making. This is crucial for applications that require immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Improved Privacy: Edge AI enhances data privacy by keeping sensitive information on local devices rather than transmitting it to centralised cloud servers. This reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data at the edge, Edge AI reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, alleviating bandwidth constraints and lowering costs. This is particularly important in scenarios with limited connectivity or high data volumes.
Scalability: Edge AI enables scalable solutions by distributing computational workloads across numerous edge devices. This decentralised approach allows for the efficient deployment of AI across large networks, such as smart city infrastructures and industrial IoT systems.
Challenges and Future Directions
While Edge AI is a potential technology, it is not without its own challenges and limitations. Professional learning must equip learners to recognise the challenges associated with the technologies they learn so that their learning is consistent with real-world situations. An inclusive Data Science Course in Chennai, for instance, will ensure that learners are made aware of these challenges and have the skills to resolve them in a manner that best suits a situation.
Some challenges that Edge AI professionals must be aware of are listed here:
Hardware Limitations: Edge devices often have limited computational power and memory compared to cloud servers. Developing efficient AI models that can operate within these constraints is a key challenge.
Energy Consumption: Processing AI algorithms locally can be energy-intensive, which is a concern for battery-powered edge devices. Innovations in energy-efficient hardware and algorithms are needed to address this issue.
Security: Ensuring the security of edge devices and data is critical, as these devices can be vulnerable to physical tampering and cyberattacks. Robust security measures, including encryption and secure boot processes, are essential.
Interoperability: Integrating diverse edge devices and ensuring seamless communication between them can be complex. Standardisation and interoperability frameworks are necessary to facilitate smooth integration.
Despite these challenges, the future of Edge AI is quite promising and Edge AI is increasingly being covered in almost any Data Science Course. Advances in hardware, such as AI accelerators and neuromorphic chips, are enhancing the computational capabilities of edge devices. Additionally, ongoing research in federated learning and distributed AI is enabling collaborative model training across multiple edge devices without sharing raw data, further improving privacy and efficiency.
Conclusion
Edge AI is bringing data science closer to the source, transforming the way we process and utilise data. By enabling real-time, localised data analysis, Edge AI is driving innovation across various industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to smart cities and autonomous vehicles. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for Edge AI to create more efficient, responsive, and secure systems is immense, paving the way for a smarter and more connected world.
BUSINESS DETAILS:
NAME: ExcelR- Data Science, Data Analyst, Business Analyst Course Training Chennai
ADDRESS: 857, Poonamallee High Rd, Kilpauk, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600010
Phone: 8591364838
Email- enquiry@excelr.com
WORKING HOURS: MON-SAT [10AM-7PM]